Table
A table allows users to view data organized in rows and columns.
Beta This component is still a work in progress. Questions or concerns? Please let us know.
Anatomy
Tables are a collection of cells arranged in a two-dimensional grid. We call the horizontal slice a row and the vertical slice a column.
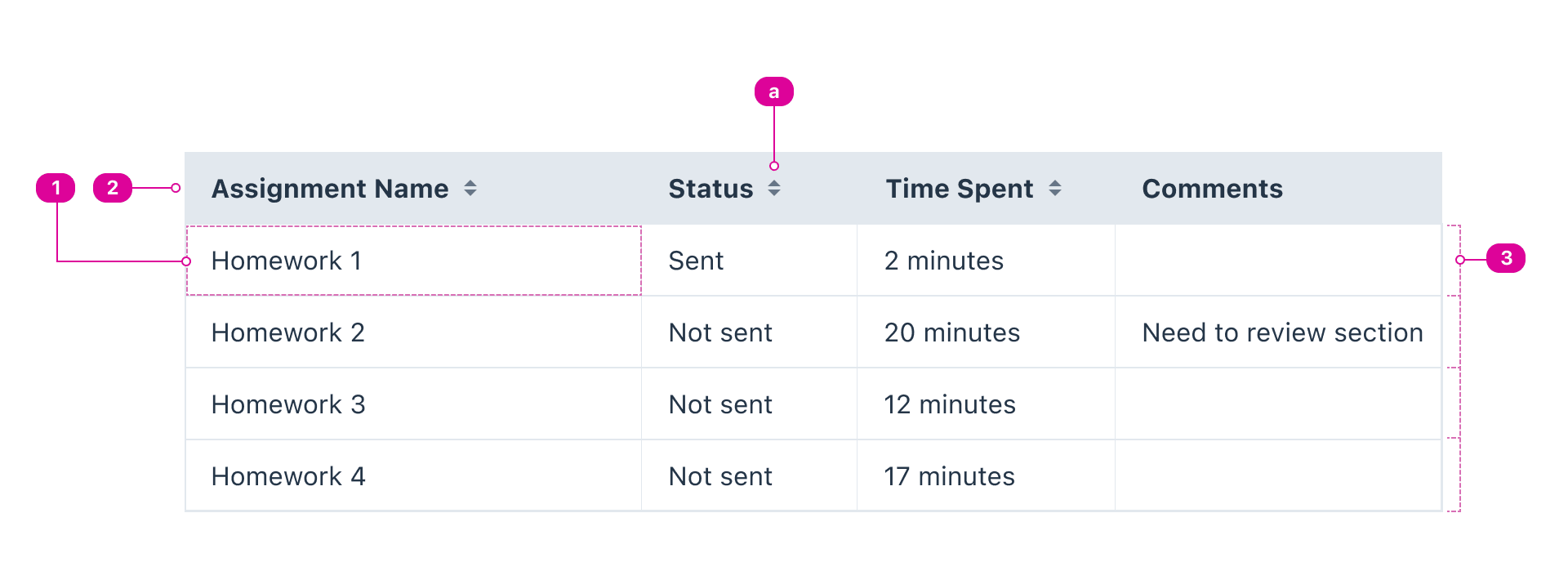
- Cell - the fundamental unit of a table. Each cell contains one piece of data.
- Header row - the first row of a table contains header cells that label the cells within their column.
- Sort indicator (required when sortable) - a visual indicator of the table's sort state, which can be ascending, descending, or unsorted.
- Body rows - the remaining rows of the table contain the data arranged in rows. Each row represents a single slice of the data.
Usage
Use a table to organize and display long lists of data or content, or to help users find a specific piece of information in a large data set.
- Table columns should be aligned based on their content type:
- Text - left align
- Numbers - right align
- Checkboxes or radio buttons - center align
- Columns should be in a logical order from left to right based on the content. The farthest left content column should meaningfully label the row. If bulk actions can be taken, a checkbox should be the first item in the column. If there are no bulk actions, the most important identifying information should be in the first column. For example, in a student set the first column should be the student's name.
- Tables must have at least 2 columns. If a table has less than 2 columns, use a list or another format to present the data so it is easier to understand the information.
- Column titles in the header row should be as short as possible, allowing wrapping to two lines if necessary, while table content should ideally fit on one line but can wrap to multiple lines when needed.
- All content within a column is the same level of hierarchy as all other content within that column. A table shouldn't be used to communicate hierarchy.
- If a table has no content, it should display an empty state or not display the table at all.
- Column titles should accurately label the data within the column, and include units of measurement in the column title if possible.
Search & Filter
Search and filters can be used in conjunction with tables to help users find information.
- If columns are sortable, the sort symbols are always visible.
- Introducing more functionality within a table will create more complexity and can lead to users having difficulty interpreting the information presented in the table.
- Don't use a table purely for layout purposes.